Found this article interesting?
If you would like personalized advice or have more questions, please contact us here.
The Definitive Guide to SEO Ranking Factors and Terms (2025 Edition)
By Jose Roman in SEO

If you've ever asked yourself why your website doesn’t show up on Google — or why your competitor seems to rank higher — then this guide is for you. SEO, or Search Engine Optimization, is the key to ranking on Google and other major search engines, such as Bing and YouTube. A short definition of SEO would be: "a group of practices and techniques that make a website appear in the search engine results pages (SERPs) of major search engines." If you’ve already done some research on how SEO works, you’ve probably found yourself navigating through a bunch of weird terms and acronyms that sound like they were pulled from a sci-fi movie. The purpose of this guide is to give you simple explanations of what those terms mean and what kind of information they provide. That way, you can better understand how your website is performing — and make more informed decisions if you ever decide to hire an SEO agency. And if you're just curious and want to know more about how Google works, this guide will help you, too. As said before, Search Engine Optimization (SEO) is the practice of improving your website so that it ranks higher in search engine results (SERPs)— especially Google. In 2025, visibility online is no optional — it's a requirement for growth. Your potential customers are searching for services and products like yours every day, and if your website isn't showing up, you're missing out on valuable traffic, leads, and sales. SEO helps your business get found by the right people at the right time, without paying for every single click. Google uses complex algorithms to determine which web pages appear at the top of search results. These algorithms consider hundreds of signals, from the quality of your content and the speed of your site, to how trustworthy other websites consider you (backlinks). While the system is constantly evolving, the goal remains the same: to show users the most relevant, useful, and trustworthy content available. Understanding these ranking factors is the first step to improving your online presence. This guide is designed to demystify SEO by clarifying common concepts, explaining them in a simple verbiage. Whether you're handling your own marketing or working with an agency like TagLine Media, knowing the fundamentals will help you make smarter decisions — and better understand why your agency recommends certain strategies. You'll learn what truly affects your rankings, which SEO terms matter (and what they really mean). No jargon. No over-complications. Just practical information you can actually use. Ready? Take your favorite drink, a few snacks and enjoy! On this Guide: Intimidated by the length of this guide? We know, we know, this guide is long and you may not have time right now to read it all the way through. That's why in this link you can download the complete guide, with additional contents, in PDF format. Ideal for you to read and consult it whenever and wherever you want. Google uses hundreds of signals to determine which pages to show first — but not all factors are created equal. Here are the ones that matter most: Google’s top priority is serving users the most relevant and valuable content for their query. That means your content should be original, well-written, and designed to answer the user’s question clearly. Tip: Write content for people first, then optimize it for search engines. Keywords help Google understand what your content is about — but just stuffing them in won’t help. It’s more important to align your content with the intent behind a search (informational, transactional, navigational, etc.). Ok, ok, but what is a "Keyword" in SEO? A keyword is the word or phrase that people type into search engines when looking for information, products, or services. In SEO, keywords help search engines understand what your content is about so they can match it to relevant search queries. For example, if someone searches for "best Italian restaurant in Tucson," Google will scan its index for pages that include and relate to that keyword. If your restaurant's website uses that phrase (naturally, not excessively), Google is more likely to show it in the results. There are different types of keywords: Effective SEO starts with understanding what keywords your audience is searching for — and then using them strategically throughout your content. Tip: Use keywords naturally in your titles, headings, and paragraphs. A slow website frustrates users and hurts your rankings. Google favors fast-loading sites with clean, optimized code and minimal delays. Wait, hosting can affect SEO? What is "caching"? Yes, your hosting can affect your SEO in multiple ways. In short, a hosting service must deliver your website's files as quickly as possible — this is what we call "page speed." How fast your website loads in a user’s browser depends, among other factors, on the features provided by your hosting provider. Caching also impacts the page speed of your website. A cache is a local memory managed by the user's browser that stores some of your website's files. The first time a user visits your site, the browser downloads all the necessary files to display it — such as HTML, PHP, CSS, JavaScript, and image files. Because of this, the first visit may take a little longer to load. However, once the browser stores those main files in its cache memory, future visits to your website will load much faster. Tip: Compress images, use caching, and choose a fast hosting provider. With the majority of users browsing on mobile, Google uses mobile-first indexing. If your site doesn’t perform well on smartphones, your rankings will suffer. Responsive design means that your website is ready to automatically adjust its layout, images sizes, and functionalities to look and work great on any device — whether it's a desktop computer, laptop, tablet, or smartphone. In other words, your website should be easy to read, navigate, and interact with no matter the screen size. Mobile-first indexing means that Google will check how a website performs on mobile devices first –and considers that aspect more important that how the same website performs on desktop. When Google analyzes a website, it takes as reference the mobile version of that website. This means Google simulates visiting your site from a smartphone in order to score its performance and determine how relevant the content is. Websites that aren’t mobile-friendly may rank lower in search results. Tip: Use responsive design and test your site on different devices. When credible websites link to your content, it signals to Google that your site is trustworthy and relevant. These are called backlinks, and they’re one of the most powerful ranking signals. In SEO, authority means how trustworthy, credible, and influential is your website for search engines — especially Google. The more authority your website has, the more likely it is to rank higher in search results. A website can increase its authority over time through things like: There are two common types of authority: Think of authority like your website’s reputation online — the more trusted and referenced it is, the more Google wants to show it to users. Tip: Earn backlinks through high-quality content and outreach. When you add a page's URL to the navigation menu or when you include a link from one page to another within your site, you're working the internal linking. A clear internal linking strategy helps both users and search engines navigate your site and understand its structure. It also distributes authority (also known as "SEO juice" or "link juice") across your pages and helps Google crawl of your website more efficiently, avoiding unnecessary use of your crawl budget. But let’s take it one step at a time — we’ve just introduced some new terms that are worth understanding. “SEO juice” (also known as link juice) is a casual term used in the SEO world to describe the value or authority that one page passes to another through a link. When a page with strong authority links to another page — either on the same site or a different one — it shares some of its SEO value, helping the linked page rank higher in search results. Crawl budget refers to the number of pages Google is willing to crawl on your site within a given period of time. Google doesn’t have unlimited time or resources, so it assigns a crawl budget to your website, based on how important and well-maintained your site is. If your site has too many unnecessary pages, duplicate content, or broken links, Google may waste time crawling the wrong things — and ignore more important pages. That’s why a clean, well-structured site with smart internal linking helps Google focus on what truly matters. Tip: Link to your main service or product pages from related blog posts. Google monitors how people interact with your site. If your site has a high bounce rate or don’t find what they’re looking for, it can affect rankings. Bounce Rate? What's that? Bounce Rate defines the percentage of visitors who arrive to your website and then leave without any interaction with it, that means, they leave without clicking, scrolling, etc. A high bounce rate usually means that users didn't find what they are looking for or the page didn't keep the user's attention. That sends a signal to Google that your page might not be helpful or relevant for the search preformed by the user (the keyword the user typed on Google search box). If this happens often, Google could assume your content isn’t matching search intent, or that the user experience isn’t great (maybe it loads slowly, looks outdated, or lacks clear direction). Over time, this can cause your rankings to drop. Tip: Make your site easy to navigate, fast to load, and simple to understand. If your business serves a specific geographic area — like Tucson, for example — then local SEO is a must. It’s all about helping your business show up when nearby customers search for services “near me” or include a location in their query. One of the biggest assets in local SEO is your Google Business Profile (GBP). This is what appears on Google Maps and in the “local pack” — those top 3 map-based results you see when searching for things like “coffee shop in Tucson” or “SEO agency near me.” But Google doesn’t just show any business in that spot. It prioritizes: If any of this info is inconsistent or incomplete, it can confuse Google — and potential customers. Tip: Make sure your business is listed on Google, Yelp, Facebook, and local directories — and that the name, address, and phone number match exactly across all of them. Gather reviews regularly and respond to them to boost engagement and trust. Tip: Embed a Google Map on your website and add location-specific keywords (like your city or neighborhood) to key pages and headings. Why embed a Google Map on your website? Embedding a Google Map on your contact or homepage gives users a quick, visual way to see where your business is located — which improves usability. But it also sends local relevance signals to Google. By embedding the map: Think of it like saying, “Hey Google, here’s exactly where we are — show us to people nearby.” Why use location-specific keywords? When you include the name of your city, neighborhood, or service area in your page titles, headings, and content, you help Google understand that your business is locally relevant. For example: This makes it more likely that your pages will appear when someone in your area searches for those services — especially in “near me” and voice searches. PRO Tip: You don’t need to overdo it — just mention your location naturally throughout your site, especially on key service and contact pages. When it comes to improving your website’s rankings, what’s on the page really matters. That includes how your content is structured, how your titles are written, what images you use, and how easily users — and search engines — can understand what your page is about. This chapter breaks down the most common on-page SEO terms you’ll hear from marketers and agencies (like us), and explains what they actually mean in plain English. But first, what does On-Page SEO means? On-Page SEO refers to all the things you can optimize directly on your website to help it rank higher in search engines. It’s everything that happens on the page — like your headlines, content, images, internal links, and even the way your URLs are written. The goal of on-page SEO is to make your pages easier for both people and search engines to understand, navigate, and trust. If your website is a house, on-page SEO is making sure the inside is clean, organized, and ready for guests — including Google. A title tag is the clickable headline that shows up in search engine results. It’s also what appears in the browser tab when someone visits your page. Example: A strong title tag should: Tip: Think of it as your page’s first impression on Google — and your potential customer. A meta description is the short paragraph that appears right below your title tag in search results. It doesn’t directly affect rankings, but it does impact whether users click on your page. Example: A great meta description: Tip: Think of it like ad copy — it’s your pitch to get the click. Need help to customize or configure your and/or ? Getting into the technical side of SEO isn’t always intuitive — and that’s totally understandable. You might be the best doctor, the best mechanic, the best landscaper, or contractor in town… but that doesn’t make you a digital marketing expert. And you shouldn’t have to be. At TagLine Media, we specialize in turning technical SEO into real-world results. Let us take care of the backend — so you can focus on what you do best. Header tags help structure your content and tell search engines what each section is about. They also make your content easier to read for users. Think of your website like a book. If the book you want to read doesn’t include structure — like titles, subtitles, chapter headings, or even an index — it becomes confusing and hard to follow. The same goes for web pages: well-organized content with clear headers makes it easier for visitors to absorb information and for Google to understand what your page is about. In addition, headers should follow a logical order of importance. For example, an H2 should always come after an H1, and an H3 should be nested under an H2, not the other way around. You shouldn’t jump from an H1 to an H4 just because it “looks good.” This hierarchy helps Google better interpret the structure of your content — and it improves accessibility for users using screen readers. Also, every header should introduce a section of text. A paragraph should always follow a header — not the other way around. Think of headers as signposts: they guide the reader through your content and tell them what to expect next. Search engines use headers to understand your content’s hierarchy. Users use them to skim and find what they need. Why should a page have only one H1? An H1 tag is meant to be the main title of the page — the top-level heading that tells both users and search engines what the entire page is about. Think of it like the title of a newspaper article or the name of a book. You only need one, and it should clearly reflect the primary topic of the page. Using multiple H1 tags can confuse search engines because it creates ambiguity: Which topic is most important? What is the page really about? While modern browsers and Google can technically handle multiple H1s without breaking your page, sticking to a single H1 is still considered best practice because: Your website’s URLs play a small but important role in SEO. A good URL structure is clean, simple, and clearly reflects the content of the page. Compare these two examples: Search engines (and humans!) prefer URLs that are easy to read. Short, keyword-rich URLs give Google a stronger signal about what your page is about — and make users more likely to click. Tip: Avoid using random numbers, special characters, or overly long slugs. Stick to lowercase words separated by hyphens. Alt text (short for "alternative text") is a written description of an image. It serves two important purposes: Example: Tip: Always describe the image accurately and, when appropriate, include relevant keywords — without stuffing. Structured data, also known as schema markup, is a special type of code added to your web pages that helps search engines understand the content in a more detailed way. It can identify things like: When implemented correctly, structured data can lead to rich results — enhanced listings in Google with star ratings, images, FAQs, and other extra info. Example: While on-page SEO focuses on content and user experience, technical SEO ensures that your website is optimized for search engines to crawl, index, and render it effectively. Think of it as the foundation that supports all your SEO efforts. Without a solid technical base, even the best content might not achieve its full potential in search rankings. In this chapter, we'll demystify essential technical SEO terms, helping you understand the behind-the-scenes elements that keep your website running smoothly and ranking well. Crawlability refers to a search engine's ability to access and navigate through your website's content. If search engines can't crawl your site, they can't index your pages, which means they won't appear in search results. Period. Tip: To check if your website is indexed by Google, go to google.com and type in the search bar: Your website doesn't appear on Google? If your website isn't showing up in search results, you're missing out on valuable traffic and potential customers. Whether it's an indexing issue, technical SEO problem, or something else, we're here to help. Contact TagLine Media today to schedule a free Technical SEO consultation. Our experts will analyze your website and provide actionable insights to improve your online visibility. Key Factors Affecting Crawlability: The robots.txt file is a text file that you can find in the root directory of your website (e.g., Key Functions of robots.txt: Example of the content of a simple robots.txt file: In this example, all user agents (denoted by The Example: Including the A broken link, also known as a dead link, is a hyperlink (🤓 just a link) that points to a page or resource, such a an image, an internal pdf document, etc, that no longer exists or cannot be accessed. When users or search engine crawlers attempt to follow a broken link, they typically encounter an error message, such as a 404 (Not Found) or 410 (Gone) status code: Common Causes of Broken Links: Why Broken Links Matter: How to Fix Broken Links: Tools to Identify Broken Links: Tip: Regularly auditing your website for broken links ensures a seamless user experience and maintains your site's SEO health. Indexability refers to a search engine's ability to analyze and add your web pages to its index. Once a page is indexed, it becomes eligible to appear in search results. Imagine your website as a book in a vast digital library. For readers (in this case, search engine users) to find your book, it needs to be cataloged correctly. In the world of search engines, this cataloging process is known as indexing, and indexability refers to how easily a search engine can analyze and add your web pages to its index. When a page is indexable, it means that search engines like Google can access, understand, and store its content in their massive databases. Once indexed, your page becomes eligible to appear in search results when users look for relevant information. However, if a page isn't indexable, it's as if it doesn't exist in the eyes of search engines. No matter how valuable or well-written the content is, it won't show up in search results, leading to missed opportunities for visibility and engagement. Key Factors Affecting Indexability: 🤨 mmm.. Canonical Tags? Canonical tags are HTML elements that help prevent duplicate content issues or cannibalization issues by specifying the preferred version of a web page when multiple versions with similar or identical content exist. By indicating the "canonical" (or master) version, you guide search engines to index the correct page, consolidating ranking signals and avoiding potential SEO pitfalls. Why Canonical Tags Matter: How to Implement Canonical Tags: Add a Or you can use a SEO plugin, such as Yoast SEO or RankMath and apply that directive with a single click. Example of a canonical tag: In this example, even if users access the page through different URLs (e.g., with tracking parameters), search engines will understand that the canonical version is Tip: Regularly auditing your site for proper canonical tag implementation helps maintain SEO health and ensures that search engines index the right content. So, how to ensure my pages are Indexable To improve your website's indexability and ensure there are no potential issues preventing your web pages from being indexed, you can check these basic aspects: Regularly auditing your website for indexability ensures that your content reaches its intended audience and supports your overall SEO goals. Wait, "submit" a sitemap? What does that mean? Don't worry—no need to panic! It's not about mailing a legal document. But first, let's start by answering the question: An XML sitemap is a file that lists all the important pages of your website, serving as a roadmap for search engines like Google to discover and index your content efficiently. It's like the table of contents of any book. By providing a structured overview of your site's URLs, an XML sitemap ensures that search engines can find and crawl your pages, even if your internal linking isn't perfect. How to Create and Submit an XML Sitemap: You saw it? it wasn't that complicated! Still confused about the indexability of your website? Don't be overwhelmed, that's what SEO experts are for! Contact us today and let's start improving the SEO of your website. Page Speed refers to the performance of your website in terms of loading speed, which means "how fast" your website loads in a browser and is served to the user. Why Does Site Speed Matter for SEO? Site speed refers to how quickly your website loads and responds to user interactions. It's a critical factor for both user experience and search engine optimization (SEO). Key Factors Affecting Site Speed Several elements can influence your website's loading time, such as large or uncompressed images, excessive code, a slow server response time, among others. Here is a summary of the most common causes of a slow web response: How can I measure the loading speed of my website? Good question, in order to analyze or measure the loading speed of your website you can use several tools, such as: How can I Improve the Site Speed of my website? Ohh my friend. That question gives for another extensive guide and is not the subject of this one you are reading. Tip: Regularly reviewing the performance and loading speed of your website is crucial to keep it up to date and detect potential performance problems early on. Is your website loading slow? A slow-loading website can frustrate visitors, increase bounce rates, and negatively impact your search engine rankings. Don't let sluggish performance hinder your online success. Reach out to our experts for a comprehensive website speed audit and discover how we can enhance your site's performance. The security of your website is another important aspect of its technical SEO performance. And it's not a matter of having your website protected from hackers. When we talk about security, from the SEO point of view, we refers to how secure is your website to your visitors. Think about it, would you be willing to enter a dangerous neighborhood? What makes a website secure? SSL (Secure Sockets Layer) is a security protocol that encrypts the data transmitted between a user's browser and your website. When a website has an SSL certificate, it uses HTTPS (Hypertext Transfer Protocol Secure) instead of HTTP, indicating a secure connection. Implementing HTTPS is crucial for several reasons: Neglecting to secure your site with HTTPS can lead to browser warnings, deter visitors, and negatively impact your SEO rankings. A web application firewall (WAF) acts as a shield between your website and potential threats. It monitors incoming traffic, blocks malicious activities, and prevents common attacks like SQL injections and cross-site scripting (XSS). Benefits of implementing a firewall include: Regularly updating and monitoring your firewall settings is essential to adapt to evolving security threats. Tip: Check the features and configuration of your hosting with your provider to verify whether or not you have a Firewall installed. At TagLine Media, our hosting service includes a Firewall by default. When it comes to improving your website's visibility and performance in search engine results, optimizing your site's content and structure (on-page SEO) and/or fixing crawlability and/or indexability issues is only part of the equation. Equally important is off-page SEO. Off-Page SEO refers to all the activities happening outside your website that enhance (or not) its authority, relevance, and trustworthiness. This includes strategies like building high-quality backlinks, earning brand mentions, and engaging with audiences on social media platforms. By effectively implementing off-page SEO tactics, you signal to search engines that your website is a credible and valuable resource, which can lead to higher rankings and increased organic traffic. Lets define some common terms regarding Off-Page SEO. A backlink is a hyperlink from one website to another. In SEO, backlinks are vital because they signal to search engines that others website found useful and valuable your website. Think of them as endorsements; the more quality backlinks your site has, the more authoritative it appears to search engines. Yes, you read that right; quality backlinks. So now you must be asking yourself that if there are quality backlinks, there must be low quality or toxic backlinks… and you are right What are "quality backlink" and "Toxic Backlinks"? Not all backlinks are created equal. Quality Links originate on reputable and relevant websites pointing to yours. Those backlinks carry more "weight" and helps to increase your domain authority. Toxic Links often originate from spammy, irrelevant websites, or manipulative sources, such as link farms, private blog networks (PBNs), or sites involved in unethical practices. Search engines like Google may interpret these links as attempts to manipulate rankings, which can lead to penalties or a decrease in your site's visibility in search results. Tip: Regularly auditing your backlink profile is essential to maintain a healthy SEO standing. Tools like Google Search Console, Ahrefs, or SEMrush can help identify and manage toxic backlinks, ensuring your site remains in good standing with search engines. Overwhelmed by toxic backlinks on your website? Through a thorough analysis and the use of the right tools, we can help you eliminate or minimize the amount of toxic backlinks your website may have. Contact our specialists today and let's start sanitizing your website! Link building is the process, strategies and tactics of acquiring backlinks from other websites to your own. Link Building is not a process that occurs by its own, it's a group of actions that a SEO expert has to perform. Some effective strategies include: Avoid black-hat techniques like buying links or participating in link farms, as these can lead to penalties from search engines. As noted in Chapter 1, Domain Authority (DA) is a metric developed by Moz that predicts how well a website will rank on search engine result pages (SERPs). It's scored on a scale from 1 to 100, with higher scores indicating a greater ability to rank. DA is calculated based on various factors, including the number and quality of backlinks. While Google doesn't use DA as a ranking factor, it's a useful comparative metric to gauge your site's SEO strength relative to competitors. An Anchor text is the clickable text in a hyperlink. Optimizing anchor text is crucial because it provides context to both users and search engines about the linked page's content. Best practices include: While social media links are typically "nofollow" and don't directly influence search engine rankings, their impact on off-page SEO is significant and multifaceted. Amplifying Content Reach Social media platforms like Facebook, Twitter, LinkedIn, or Instagram serve as powerful channels to distribute your content to a broader audience. By sharing engaging content, you increase the chances of it being seen, shared, and linked to by others, which can lead to the acquisition of high-quality backlinks from various websites, alongside with organic traffic to your website. Enhancing Brand Visibility and Authority Active engagement on social media helps build your brand's presence and authority. When users consistently encounter your content across different platforms, it reinforces brand recognition and trust. This increased visibility can lead to more branded searches and mentions, signaling to search engines that your brand is reputable and relevant. Driving Referral Traffic Sharing content on social media can drive significant referral traffic to your website. Each visit from a social platform is an opportunity to engage users, encourage conversions, and potentially earn backlinks if they find your content valuable enough to reference on their own sites or blogs. Generating Social Signals Social signals, such as likes, shares, comments, and mentions, indicate user engagement and content popularity. While search engines may not use these signals as direct ranking factors, they can influence SEO indirectly by increasing content visibility and the potential for backlink generation. Best Practices for Leveraging Social Media in Off-Page SEO Incorporating Social Media Management into your off-page SEO efforts not only enhances your online presence but also fosters community engagement and trust, all of which contribute to improved search engine visibility. Overcome by the management of your social networks? Don't blame yourself! You're a top professional in your field, and you don't need to be an expert in managing your company's social media. That's what Social Media and Online Reputation management experts like TagLine Media Group are here for. Let us handle your social media management so you can focus on what you do best and what brings the most value to your business. When we search for services on the Internet, it is very likely that we want to find them near us. If you are looking for a florist to give a bouquet of flowers to your wife or your mother, or if you are looking for a gift store to buy something for a friend, if you need the services of a locksmith or a plumber, it is normal that we want to find a solution as close as possible to where we live or where we are at that moment. Let's imagine that we are the owner of that flower shop, or that gift store, or that locksmith or plumber and that, like us, there are hundreds of other professionals like us offering the same services in the same geographic area. This example illustrates the behavior of the average user. How to stand out? This is where Local SEO comes into play. Local SEO (Search Engine Optimization) is a digital marketing strategy aimed at enhancing a business's visibility in local search results on platforms like Google. It involves optimizing your online presence to attract more business from relevant local searches, such as "best coffee shop near me" or "plumber in Tucson." This optimization ensures that your business appears prominently when potential customers in your vicinity are searching for the products or services you offer. Key components of Local SEO include: Implementing effective Local SEO strategies is crucial for businesses aiming to attract nearby customers and stand out in their local markets. The Google Business Profile (GBP) is a free tool that allows businesses to manage their online presence across Google Search and Maps. An optimized GBP enhances visibility in local search results, provides essential business information to potential customers, and facilitates engagement through reviews and updates. Maintaining an accurate and complete GBP is crucial for attracting local customers and improving search rankings. Products and Services in GBP An effective way to provide more information about your business to users (and Google) is by creating products or services in your business profile. For instance, if you operate a local garage, you can add entries for services like "Oil Change," "Tire Services," or "Brake Repair." Each listing allows you to include a brief description, where incorporating relevant keywords can enhance your visibility in search results. By detailing your offerings, you not only inform potential customers but also improve your business profile's performance in local searches. Regular Updates on GBP Regularly posting updates on your Google Business Profile (GBP) is a powerful way to enhance your local SEO and engage with potential customers. These updates can include information about your services or products, promotions, events, or even recent blog posts. By consistently sharing fresh content, you signal to Google that your business is active and relevant, which can positively impact your visibility in local search results. Moreover, engaging posts can attract more clicks and interactions, further boosting your profile's performance. To maximize the benefits, aim to post updates 1–2 times per week. Ensure each post is informative, includes relevant keywords, and features high-quality images or videos to capture attention. Incorporating clear calls-to-action, such as "Learn More" or "Call Now," can also encourage customer engagement. By maintaining an active and informative GBP, you not only improve your online presence but also build trust with your local audience. PRO Tip: Geo-Locate your images before posting them into your GPB. That will helps Google to "locate" physically your business increasing the chances of being displayed on "Images" searches and in the Google Maps' results. Local citations are mentions of your business's Name, Address, and Phone number (NAP) on various online platforms, such as directories and social media. NAP consistency across these platforms is vital for local SEO, as inconsistencies can confuse search engines and potential customers, negatively impacting your search visibility. Ensuring uniform NAP information helps establish trust and authority in your local market. What is a "directory"? A directory is a website that compiles and categorizes information about businesses, typically organized by industry, location, or activity. Examples include platforms like Yelp, Houzz, and Yellow Pages. These directories serve as valuable resources for users seeking specific services or products in their area. Listing your business in relevant directories enhances your visibility in search engine results, increasing the likelihood of attracting potential customers. However, it's crucial to maintain NAP consistency—ensuring your Name, Address, and Phone number are identical across all platforms. Inconsistencies can confuse search engines and users alike, potentially leading to lower search rankings or diminished trust in your business. At TagLine Media Group, our SEO packages include meticulous management of your business's NAP information. We ensure accuracy and consistency across your website and all directory listings, strengthening your local online presence and enhancing your visibility to prospective customers. The Local Pack, also known as the Map Pack, is a prominent feature in Google's search results that displays a map and a list of three local businesses relevant to the user's query. Appearing in the Local Pack can significantly increase your business's visibility and attract more local customers. Optimizing your GBP, gathering positive reviews, and ensuring NAP consistency are key factors in securing a spot in the Local Pack. Customer reviews play a significant role in local SEO. Positive reviews enhance your business's credibility, influence purchasing decisions, and can improve your rankings in local search results. Encouraging satisfied customers to leave reviews and responding to them demonstrates engagement and builds trust with both customers and search engines. Tip: We encourage you to include in your sales strategy the proactive solicitation of reviews from your customers. You can hand out thank you cards to your customers and provide a QR code linked to your GBP profile, where your customer can leave them a review. Why is important to reply to clients' reviews? Responding to customer reviews is a vital component of effective online reputation management and plays a significant role in enhancing your business's visibility and credibility. Engaging with customer reviews signals to search engines like Google that your business is active and values customer feedback. This interaction can positively influence your local search rankings, making your business more visible to potential customers in your area. Acknowledging reviews—both positive and negative—demonstrates that you value your customers' opinions. This responsiveness can foster trust and encourage repeat business, as customers feel heard and appreciated. Customer reviews offer insights into what's working well and what might need improvement in your products or services. Responding to reviews allows you to address concerns, correct misinformation, and showcase your commitment to continuous improvement. When customers see that you actively respond to feedback, they may be more inclined to leave their own reviews, knowing their voices will be heard. An increase in reviews can enhance your business's online presence and attract more potential customers. Addressing negative reviews professionally shows that you're committed to resolving issues and improving customer experiences. This approach can mitigate the impact of negative feedback and even turn dissatisfied customers into loyal ones. Tip: Incorporating a strategy to regularly monitor and respond to customer reviews can significantly benefit your business's reputation and growth. On this section we'll cover the basics about the most useful (and free) tools to monitor the SEO performance of your website. A must-have tool that provides insights into your website's search traffic and performance. It helps you monitor indexing status, identify crawl errors, and understand which queries bring users to your site. Offers comprehensive data on user behavior, traffic sources, and conversion metrics. It's essential for understanding how visitors interact with your site and for measuring the effectiveness of your SEO strategies. Helps you discover new keywords related to your business and see estimates of the searches they receive and the cost to target them. It's useful for keyword research and planning your content strategy. Analyzes your website's speed and provides suggestions for improvement. Page speed is a critical factor in user experience and SEO rankings. Do you want to get the content of this SEO guide in PDF, along with the extended content of chapter 6? Get all this guide in PDF format, ideal to consult it whenever and wherever you want. In addition, the PDF guide includes the extended content of chapter 6, where we explain the basic use of these SEO tools and explain the basic concepts related to them so you can use them yourself. Just click on the button! SEO can be a bit intimidating, but with the right mindset and a clear understanding of the basics, you'll have taken a big step towards a better understanding of how it works and why actions and decisions are made within an SEO strategy. This guide is going to be helpful to you, whether you want to work on your own website's SEO or you're trying to understand what your marketing team is doing. But let's face it: SEO is a long-distance race, a long game, and the digital landscape is constantly changing. Algorithms evolve, competitors adapt and best practices keep changing. That's where having a team of experts can make all the difference. A professional SEO agency brings the strategy, expertise and up-to-date tools needed to keep your website competitive and your business growing. Ready to dive deeper? Download the full PDF version of this guide, with additional content on how to use some of the most popular free SEO tools. It's our way of helping you make better decisions.Introduction
However, that definition doesn’t tell you much about what it really means to “do SEO.”What SEO is and why it matters for businesses in 2025
How Google ranks websites: a brief overview
What this guide will help you learn (and why it’s useful whether you’re DIY-ing or working with an agency)

Chapter 1: Core SEO Ranking Factors You Should Know
1. Content Quality and Relevance
2. Keywords and Search Intent
3. Page Speed and Technical Performance
What is "Caching" or "cache memory"?
4. Mobile-Friendliness
What is "responsive design"?
What means "mobile-first indexing"?
5. Backlinks and Authority
What does "Authority" mean in SEO?
6. Internal Linking and Site Structure
What is “SEO Juice” or "Link Juice"?
And what’s “Crawl Budget”?
7. User Experience (UX) Signals
8. Local SEO Signals
Chapter 2: On-Page SEO Terms and Their Meaning
1. Title Tag
<title>TagLine Media: Full Service Marketing Agency Tucson</title>
2. Meta Description
“SEO, Paid Advertising (SEM), Web Design, Social Media, and Creative Services to grow your business. Schedule your FREE Consultation. We drive companies like yours to success.”

3. Header Tags (H1, H2, H3...)
4. URL Structure
✔ taglinegroup.com/seo-services-tucson
✘ taglinegroup.com/page?id=1234
5. Alt Text for Images
Instead of leaving an image blank or naming it “img_003.jpg,” use alt text like:
“Professional podcast studio in Tucson for audio podcasting with chairs for up to 4 people”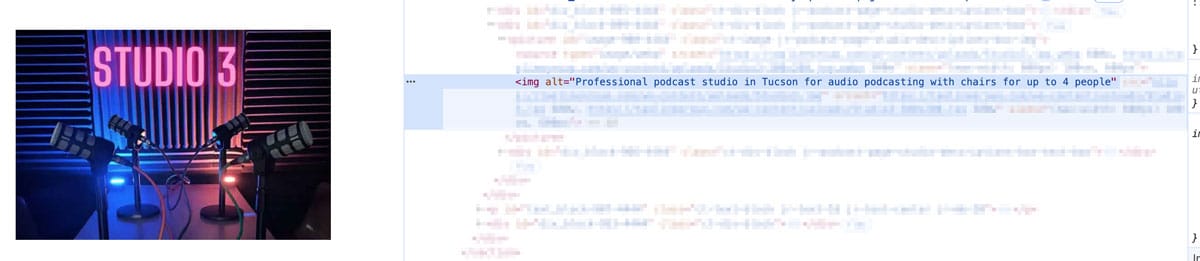
6. Structured Data / Schema Markup
If you mark up your services page with local business schema, Google may show your phone number, hours, and location directly in the search result.
Chapter 3: Technical SEO Terms and Their Meaning
1. Crawlability
site:your-website.com (replace "your-website.com" with your actual domain). If your website's pages appear in the search results, that's great — it means your site is indexed!
What is the "Robots.txt" file?
www.example.com/robots.txt) that provides instructions to web crawlers, like Google, about which pages or sections of your website should or should not be crawled.
User-agent: *
Disallow: /internal/
Allow: /
Sitemap: https://www.example.com/sitemap.xml*) are disallowed from accessing the /internal/ directory but are allowed to crawl the rest of the site.Sitemap Directive in robots.txt
Sitemap directive in your robots.txt file serves as a guidepost for search engine crawlers, indicating the location of your website's sitemap. This is particularly useful because:
robots.txt file upon visiting a website. Including the sitemap's location here ensures that crawlers can promptly find and process it.https://www.example.com/sitemap.xml), others might store it in subdirectories or use unconventional naming conventions. By specifying the exact path in the robots.txt, you eliminate any guesswork for crawlers.robots.txt file.Sitemap: https://www.example.com/sitemap.xml
Sitemap: https://www.example.com/blog/sitemap.xmlSitemap directive is a best practice that enhances the efficiency of search engine indexing, ensuring that all your site's content is discoverable.What is a broken link and how it can be fixed?
2. Indexability
noindex directive in a page's meta tag tells search engines not to index that page. By default, a new created page doesn't have to have that directive enabled but you should know it in case you detect that a page within your website is not indexed.What is a Canonical Tag?
<link rel="canonical" href="https://www.example.com/preferred-page" /> tag within the <head> section of your HTML. Ensure that each page either self-references or points to the correct canonical URL.<link rel="canonical" href="https://www.example.com/product-page" />https://www.example.com/product-page.
What is an XML Sitemap?
sitemap.xml) to your website's root directory. If you create you sitemap.xml file with an online generator, you'll have to upload to your website manually.

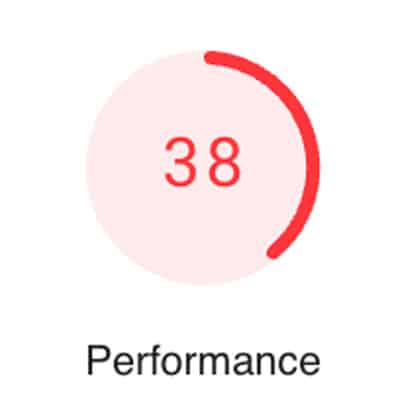
At TagLine we can perform an SEO audit and determine the reasons why your website is not correctly indexed.3. Site Speed
However, without going into too much detail, you can follow these steps to improve the performance of your website:
4. Website Security and SEO
So why would a user enter your website if it is not secure?
Moreover, today's browsers do not access unsafe websites without displaying a very explicit warning to the user.
An insecure website today means ZERO web traffic.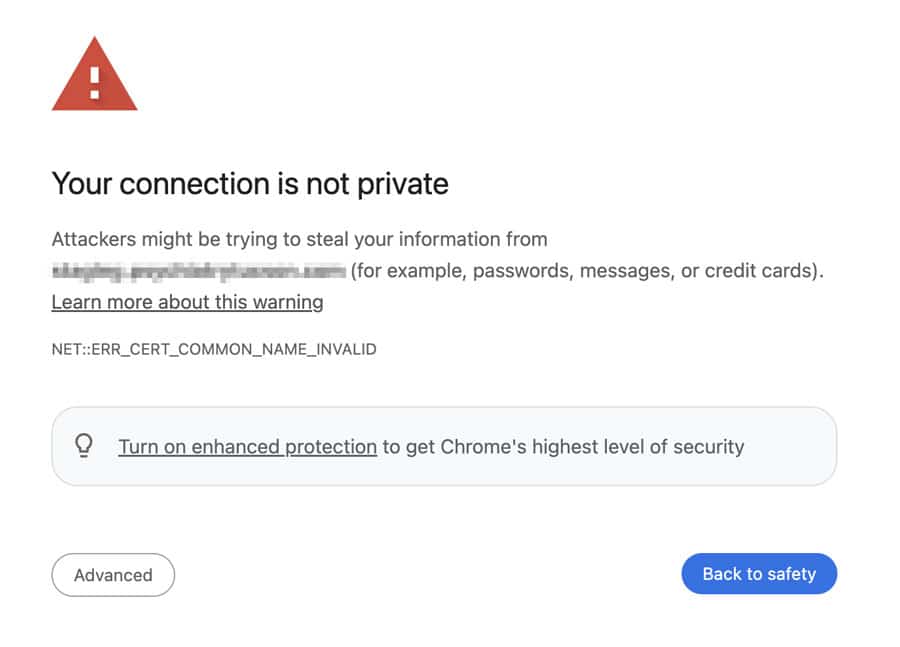
There are several tools and services that allow a website to be secure for the user who visits it. Among these tools are the SSL security certificates, the secure http protocol (https) and firewalls.SSL and HTTPS: Securing Your Site

Firewalls: Protecting Your Website
Chapter 4: Off-Page SEO Terms and their Meanings
1. Backlinks

2. Link Building
3. Domain Authority
4. Anchor Texts
5. The Role of Social Media in Off-Page SEO

Chapter 5: Local SEO and the Power of Google Business Profile
Now let's switch places and put ourselves in the shoes of the entrepreneur.What is Local SEO?
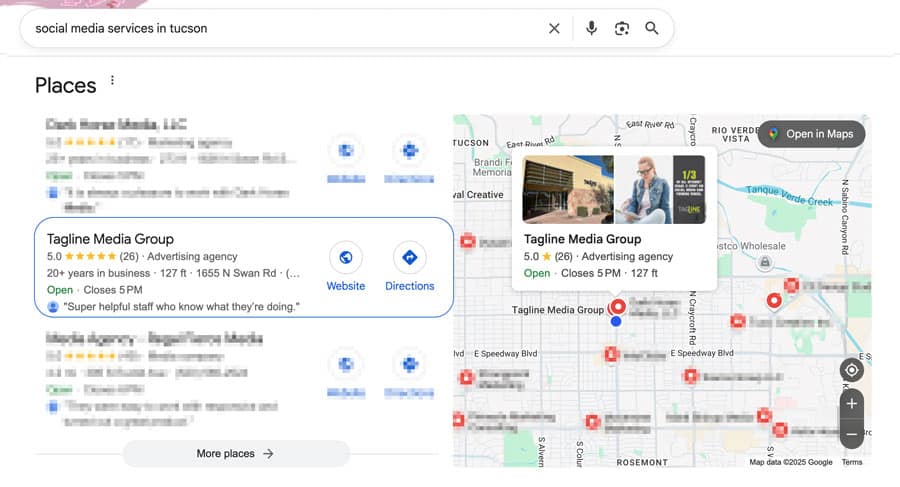
1. What is Google Business Profile (GBP) and Why It's Critical for Local Businesses
2. Local Citations and NAP Consistency
3. The Local Pack (or Map Pack)
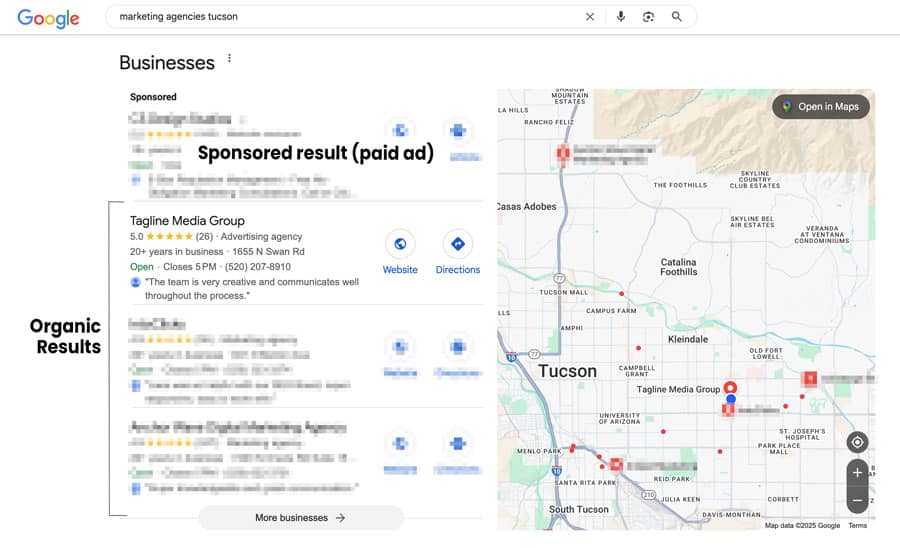
4. Customer Reviews and SEO
1. Enhances Local SEO Performance
2. Builds Trust and Customer Loyalty
3. Provides Valuable Insights
4. Encourages More Reviews
5. Demonstrates Professionalism and Accountability
Bonus Chapter 6: Essential Free SEO Tools to Monitor and Improve your Website
1. Google Search Console
2. Google Analytics
3. Google Keyword Planner
4. Google PageSpeed Insights

Final Thoughts: Build Smart, Rank Smarter
Still have questions or specific needs? we're ready to assist! Reach out to us for personalized advice and solutions tailored to your business.



